HideMee Background Remover: Complete Breakdown of Tools, Technologies, and Use Cases
In the modern digital workflow, clean visual assets are no longer optional — they are essential. From content creators to software engineers, from UX designers to e-commerce sellers, image background removal is one of the most common, yet crucial, operations.
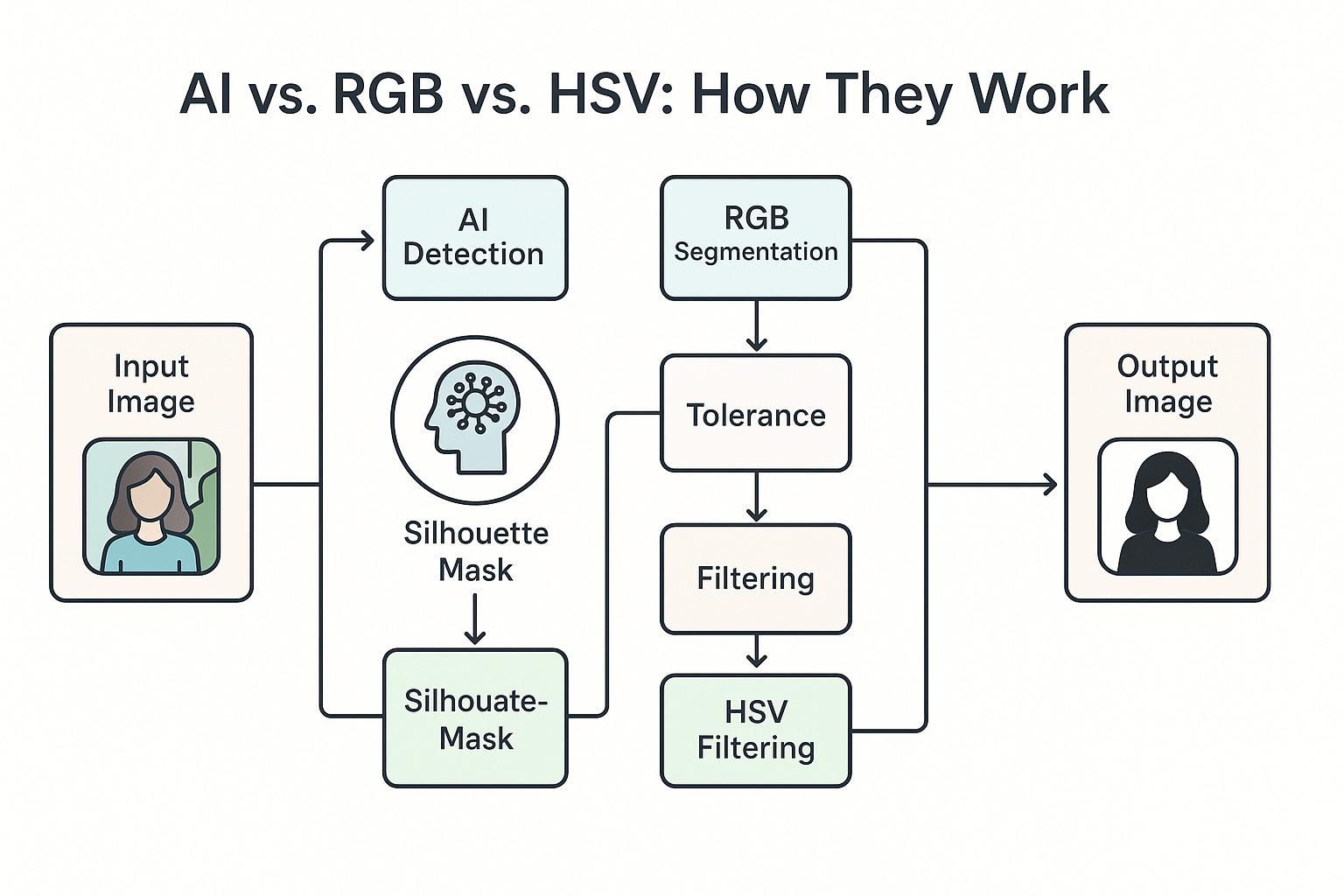
HideMee is a browser-based tool that simplifies this task using a combination of artificial intelligence, pixel-based segmentation, and manual color filtering. This article provides a detailed breakdown of how each HideMee component works, why it matters, and when to use which technique depending on your scenario.
Key Features of HideMee
HideMee provides users with a streamlined, intuitive interface that’s fully browser-based — no installation or account needed. Its core value lies in blending automation with manual control, making it useful for both casual users and professionals.
- AI-based object detection to automatically isolate subjects
- RGB/HSV filtering for manual fine-tuning
- 100% browser-based, no downloads
- Mobile-optimized interface
- Instant preview and one-click export
How These Technologies Work?
When you upload an image, a deep-learning model examines every pixel to determine which elements belong to the foreground (your subject) and which belong to the background. It uses learned patterns of shapes, textures, and edges to generate a precise binary mask that outlines the subject. Once the mask is created, the system applies it to the original image—removing or making the background transparent—and then either delivers a clean cutout or composites the subject onto a new backdrop. The entire process happens in seconds, giving you a ready-to-use subject isolated from any unwanted surroundings.
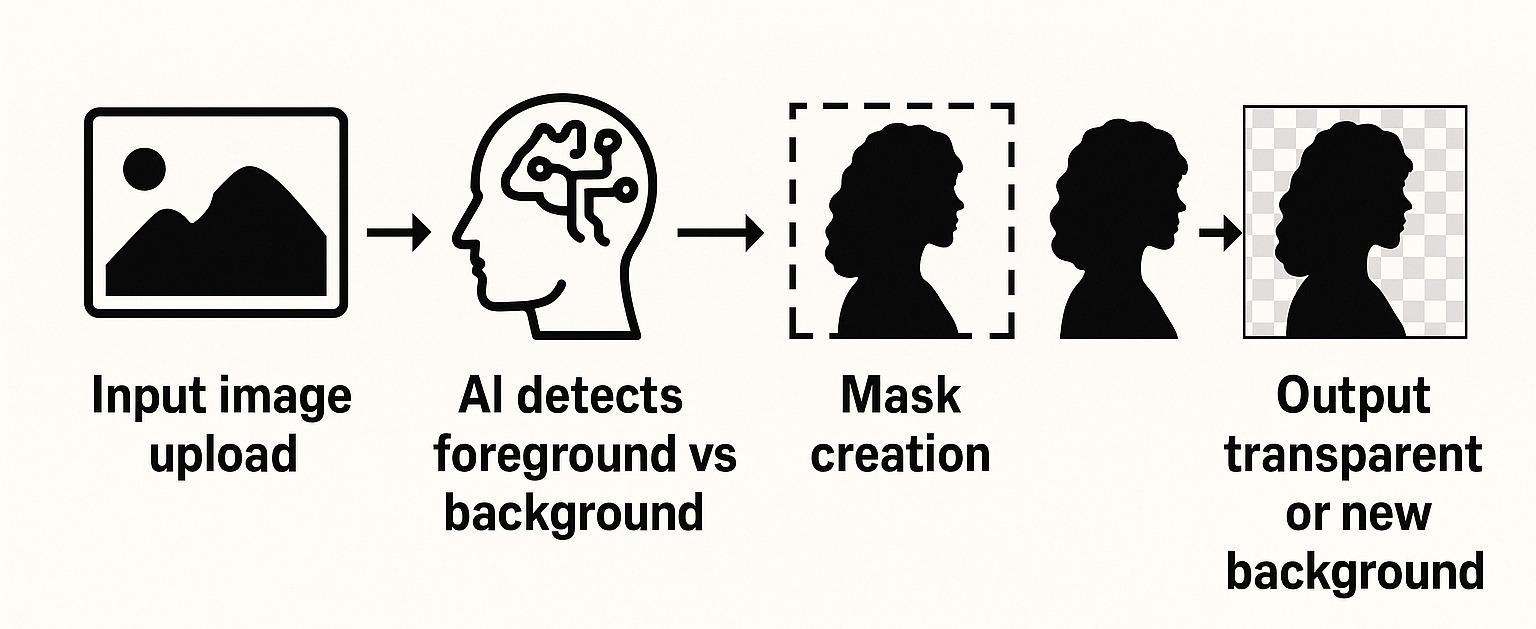
1️⃣ AI-Powered Background Removal
This method uses deep learning-based semantic segmentation, where an AI model identifies and separates the foreground (usually a person, product, or object) from its background by understanding the context of the image — not just the colors.
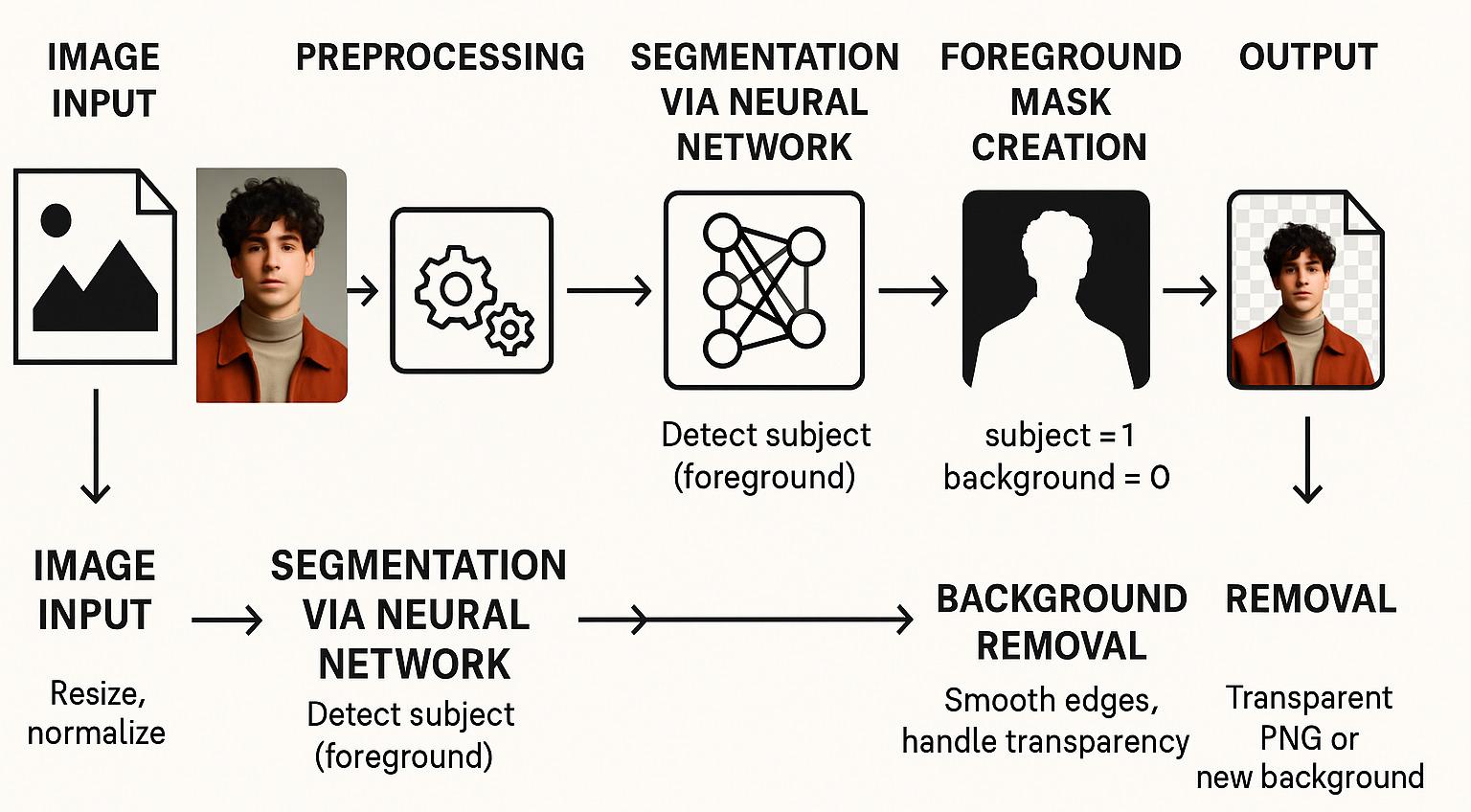
How does it work?
The system is trained on millions of annotated images, allowing it to:
- Identify common objects such as humans, animals, and items
- Understand shape boundaries and depth perception
- Detect and remove noisy, cluttered, or inconsistent backgrounds
After detection, a binary mask is applied to the image, where the background is made transparent or replaced.
When should you use it?
- When dealing with cluttered or multicolor backgrounds
- When shadows, lighting variation, or background noise make color-based removal unreliable
- When working with images that involve complex human features or group photos
Advantages
- No need for manual tuning
- High success rate in complex scenarios
- Works well across diverse image types
2️⃣ RGB Color-Based Segmentation
The RGB model breaks down an image into its Red, Green, and Blue components. Each pixel has a value between 0 and 255 in each channel. With RGB segmentation, users define a range or tolerance for one or more of these color channels.
This method allows you to define a color range by selecting a base color (e.g., green) and setting tolerance thresholds. Every pixel that falls within this range gets filtered out.
It's perfect for photos with clear contrast — like product shots on green screens or social media content with bright backgrounds.
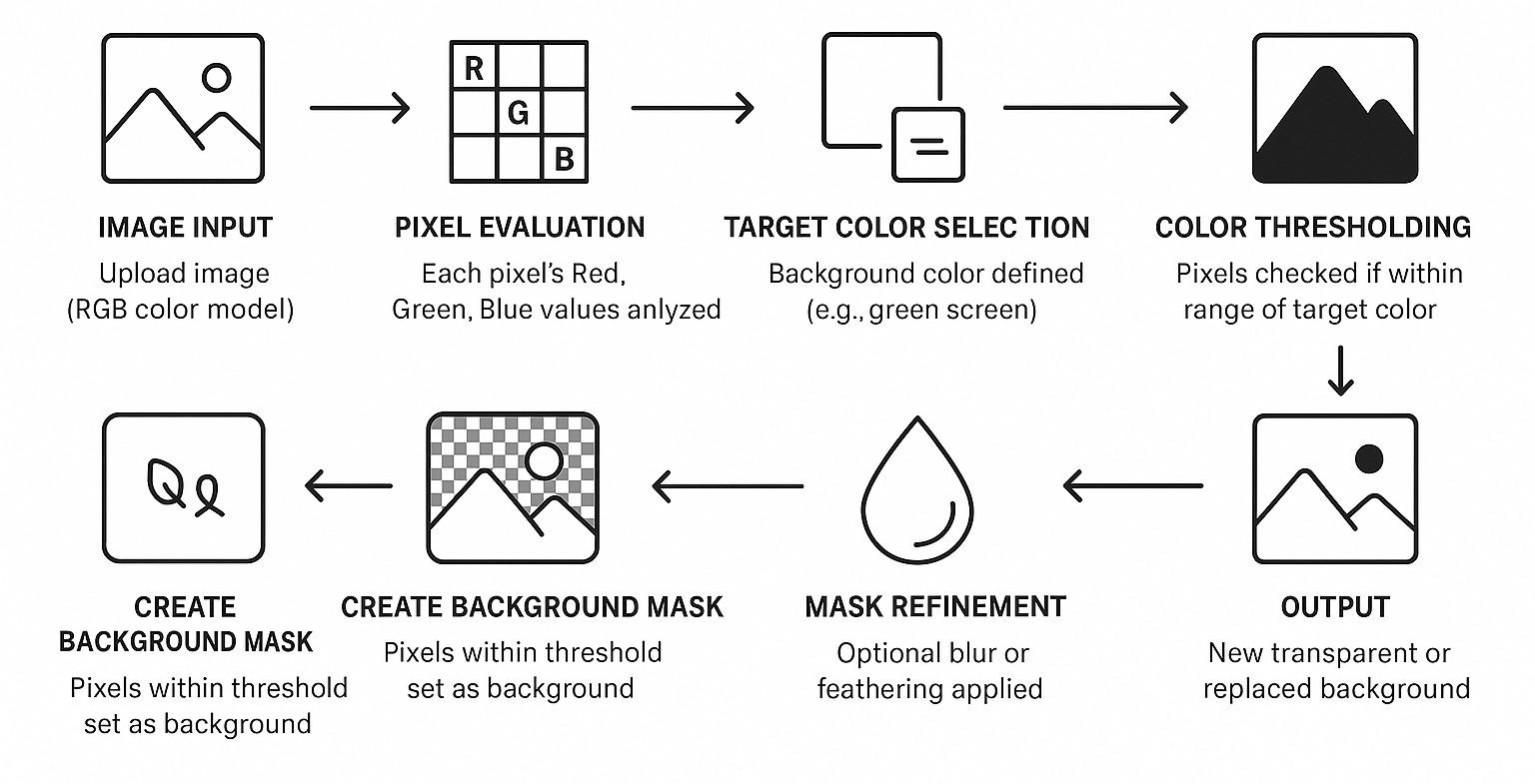
How does it work?
You can manually set a reference color (for example, the background is green: R=0, G=255, B=0). Then, define a threshold like ±20 for each channel. Any pixel within that color range is masked out.
When should you use it?
- When the background is a uniform color (like a green screen)
- When the image has a high contrast between subject and background
- When batch processing similar studio-style images
Advantages
- Extremely fast
- No training data needed
- Simple and predictable control for specific tasks
3️⃣ HSV (Hue, Saturation, Value) Filtering
HSV is a more human-centric color model compared to RGB. Instead of using red/green/blue values, it separates color information into:
- Hue: The actual color (0–360 degrees)
- Saturation: The intensity of the color
- Value (Brightness): How light or dark the color is
The HSV model mimics human color perception. It breaks down color by type (hue), intensity (saturation), and brightness (value). You can target subtle tones and refine edges more effectively than RGB.
Use this when dealing with low-contrast scenes, skin tones, or soft transitions like gradients or shadows. This makes it ideal for fine-tuning specific tones, like skin, sky, or faded fabrics.
- More control for designers and photographers
- Especially useful for portrait and natural scenery edits
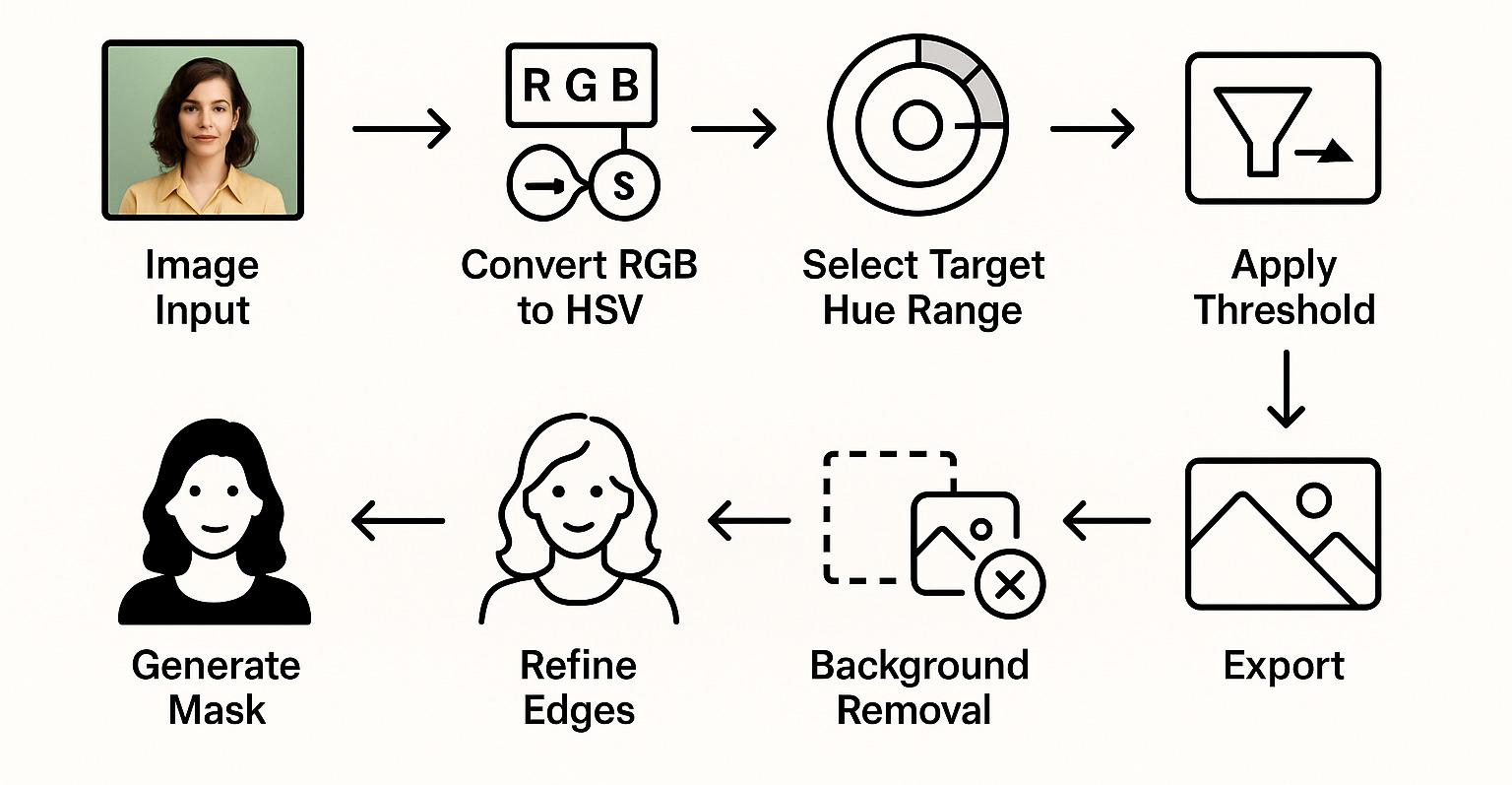
How does it work?
After converting the image from RGB to HSV:
- You select a hue range to mask (e.g., 25–40 for skin tones)
- You adjust saturation and brightness thresholds to include only relevant parts
- The background is removed based on these selections
When should you use it?
- When needing precise selection of a narrow color band (e.g., a pale sky, light clothing)
- When working with low-light or poorly lit images
- When color nuance is important (e.g., detecting subtle tones in fashion photography)
Advantages
- More intuitive than RGB for non-programmers
- Better handling of similar-looking but subtly different areas
- Works well in both bright and dark image environments
When Should You Use AI, RGB, or HSV?
Cluttered backgrounds (indoor or outdoor): When your photos have lots of overlapping objects, varied textures, or busy scenery, AI-based background removal is your best bet. Its deep learning models can distinguish complex shapes and separate foreground from background more accurately than simple color-based methods.
Use Case: Cluttered background (indoor/outdoor)
AI Detection: Best
RGB Segmentation: Poor
HSV Filtering: Moderate
Uniform green/white/blue screens: If you’re shooting against a perfectly even backdrop—like a green or blue screen in a studio—color-channel segmentation (RGB) works flawlessly. HSV filtering can also do well here, but pure RGB thresholding tends to be the simplest and fastest.
Use Case: Uniform green/white/blue screen
AI Detection: Poor
RGB Segmentation: Best
HSV Filtering: Best
Skin-tone detection: When you need to isolate people or faces—especially to preserve delicate contours and natural gradients—HSV filtering shines. By targeting just the right hue, saturation, and brightness bands, it captures subtle variations in skin tones more reliably than RGB or AI in many cases.
Use Case: Skin tone detection
AI Detection: Moderate
RGB Segmentation: Moderate
HSV Filtering: Best
Shadows and low-light conditions: In poorly lit or shadow-filled shots, AI detection again has the edge. Its trained models can infer what’s foreground even when colors and contrasts are weak, whereas RGB thresholds often fail and HSV is only moderately effective.
Use Case: Shadows and low-light
AI Detection: Best
RGB Segmentation: Poor
HSV Filtering: Good
Batch studio product shots: For consistent, high-contrast product photography—where lighting and background are controlled—RGB segmentation is ideal. It’s fast, predictable, and scales effortlessly to hundreds of images.
Use Case: Batch studio product shots
AI Detection: Moderate
RGB Segmentation: Best
HSV Filtering: Moderate
Fine color tweaking or correction: When you’re not removing the background but adjusting or filtering by a narrow color band—say, tweaking sky blues or product accent colors—HSV filtering gives you the most intuitive, precise control.
Use Case: Color correction/tweaking
AI Detection: Poor
RGB Segmentation: Good
HSV Filtering: Best
| Use Case | AI Detection | RGB Segmentation | HSV Filtering |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cluttered background (indoor/outdoor) | Best | Poor | Moderate |
| Uniform green/white/blue screen | Poor | Best | Best |
| Skin tone detection | Moderate | Moderate | Best |
| Shadows and low-light | Best | Poor | Good |
| Batch studio product shots | Moderate | Best | Moderate |
| Color correction/tweaking | Poor | Good | Best |
In short:
- AI detection is your go-to for complexity and low light.
- RGB segmentation excels on uniform, high-contrast backgrounds and bulk processing.
- HSV filtering is perfect for nuanced color work and skin-tone isolation.
Common Use Cases
- E-commerce: Standardizing product backgrounds for Amazon, Etsy, or Shopify
- Professional headshots and profile banners
- Educational slides, tutorials, training decks
- Research visualizations and clinical photography
- Creating thumbnails and removing messy backgrounds for influencers or vloggers. Digital art, memes, and creative content
- Marketing: Generating banners, profile cards, and ad creatives
- Healthcare & Research: Isolating elements in diagnostics, wound imaging, or specimen photos
- Agritech & Drones: Segmenting crops and soil in drone-based imagery
Conclusion
HideMee makes background removal fast, reliable, and customizable. Whether you're doing product edits, cleaning up personal photos, or building creative projects, HideMee gives you the automation you want — and the control you need.
In short:
- AI detection is your go-to for complexity and low light.
- RGB segmentation excels on uniform, high-contrast backgrounds and bulk processing.
- HSV filtering is perfect for nuanced color work and skin-tone isolation.
Images © Shah — released under CC0 Public Domain License .